MCP Federation
Expose a single MCP endpoint that aggregates tools from multiple backend servers with unified security.
What you’ll build
In this tutorial, you’ll:
- Configure Agent Gateway to federate multiple MCP servers
- Combine filesystem and memory servers into a single endpoint
- Access tools from both servers with automatic name prefixing
- Test federated tools in the Playground
Prerequisites
- Node.js installed
Step 1: Install Agent Gateway
curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/agentgateway/agentgateway/refs/heads/main/common/scripts/get-agentgateway | bashStep 2: Create the config
cat > config.yaml << 'EOF'
binds:
- port: 3000
listeners:
- routes:
- policies:
cors:
allowOrigins: ["*"]
allowHeaders: [mcp-protocol-version, content-type, cache-control]
exposeHeaders: ["Mcp-Session-Id"]
backends:
- mcp:
targets:
- name: filesystem
stdio:
cmd: npx
args: ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem", "/tmp"]
- name: memory
stdio:
cmd: npx
args: ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-memory"]
EOFStep 3: Start Agent Gateway
agentgateway -f config.yamlYou should see:
INFO agentgateway: Listening on 0.0.0.0:3000
INFO agentgateway: Admin UI available at http://localhost:15000/ui/Step 4: View backends in the UI
Go to http://localhost:15000/ui/ and click Backends to see your federated MCP servers:
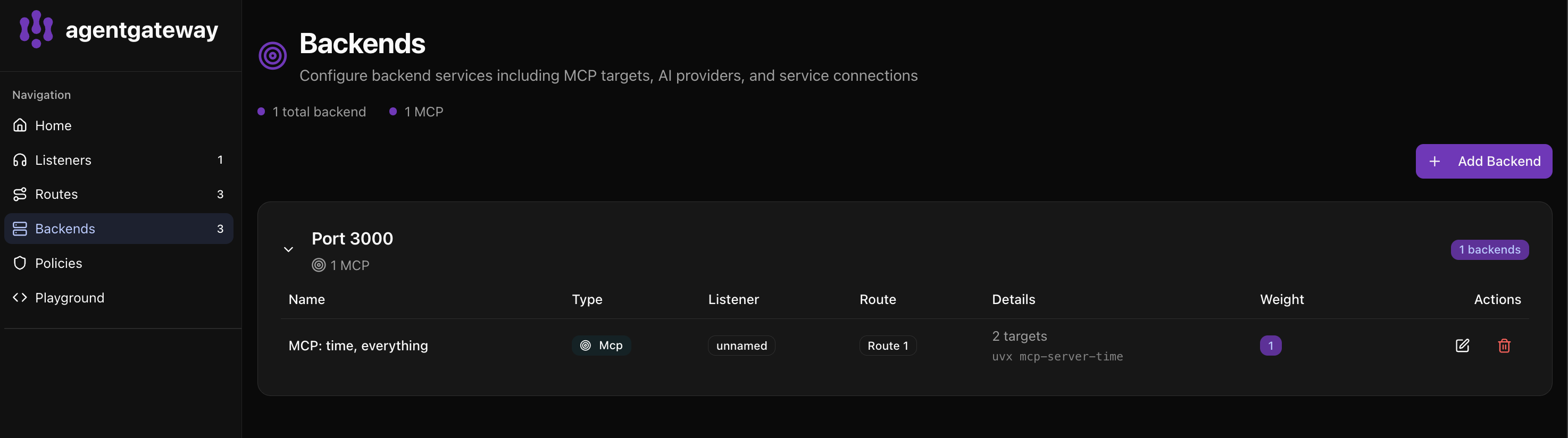
The UI shows:
- 1 total backend with 1 MCP configuration
- MCP: filesystem, memory - Both servers combined into one backend
- 2 targets - The filesystem and memory MCP servers
Step 5: Test in the Playground
Click Playground to test your federated tools:
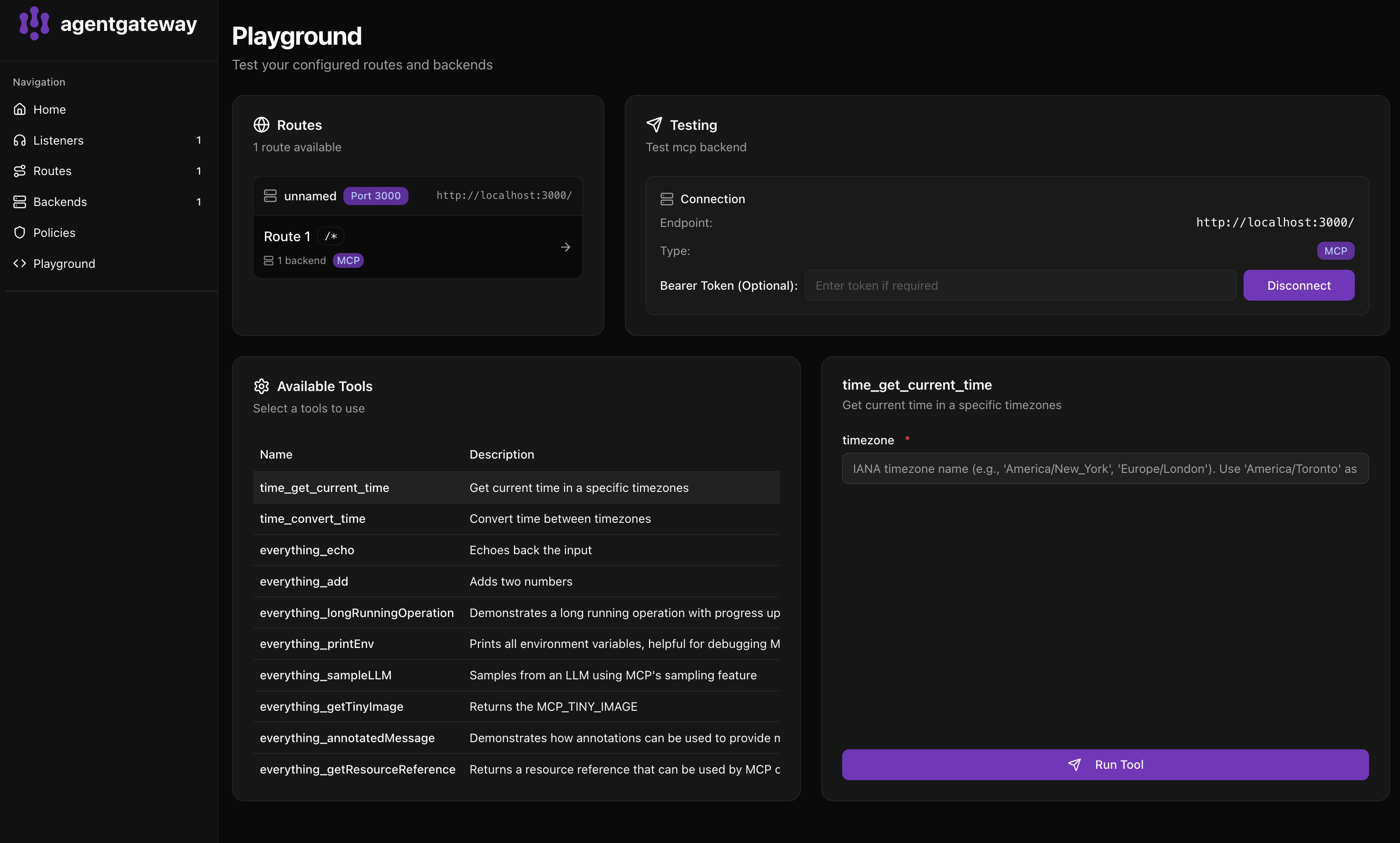
- Select Route 1 in the Routes panel
- Click Connect to discover all tools
- Available Tools shows tools from both servers:
filesystem_read_file- Read the complete contents of a filefilesystem_read_text_file- Read file contents as textfilesystem_write_file- Create or overwrite a filefilesystem_list_directory- List directory contents- And more…
Notice tools are prefixed with their server name (filesystem_ and memory_).
Step 6: Run a tool
- Click on filesystem_read_text_file in the Available Tools list
- Enter a path (e.g.,
/tmp/test.txt) - Click Run Tool
You’ll see the file contents in the response panel.
Adding more servers
Add GitHub tools (requires a token):
export GITHUB_TOKEN=your-github-tokentargets:
- name: filesystem
stdio:
cmd: npx
args: ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem", "/tmp"]
- name: github
stdio:
cmd: npx
args: ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-github"]
env:
GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN: "${GITHUB_TOKEN}"