Set up MCP auth
Secure your Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers with OAuth 2.0 authentication by using agentgateway and an identity provider like Keycloak.
About this guide
In this guide, you explore how to configure the agentgateway proxy to protect a static MCP server with MCP auth by using Keycloak as an identity provider. To authenticate with the MCP server, MCP clients such as the MCP inspector tool, can dynamically register with the identity provider to obtain a client ID. Then, the MCP client uses the client ID during the OAuth flow to obtain the JWT token. Finally, the MCP client uses the JWT token to authenticate with the MCP server and access its tools.
MCP auth vs JWT auth
You can configure both MCP and JWT auth with an AgentgatewayPolicy. For most MCP cases, choose MCP auth.
MCP auth: Use MCP auth for MCP clients, such as MCP Inspector, VS Code, or Claude Code that need to dynamically discover the auth server and register with your IdP to get a client ID. The agentgateway proxy facilitates the discovery and client registration process between MCP clients and IdPs that do not implement the MCP OAuth spec. This way, your MCP clients successfully obtain a client ID to complete the OAuth flow.
JWT auth: Use basic JWT auth when you have static clients or service-to-service traffic. Clients already have a JWT from your IdP or a static token. You only need the gateway to validate the token and optionally enforce RBAC by claims. For example, you might want to grant access only to JWTs that contain the
suborteamclaim. No discovery or client registration is involved.
Review the following table for a quick comparison of MCP auth and JWT auth.
| Feature | MCP Auth | JWT Auth |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Full MCP OAuth flow (discovery, client registration, token validation) | Validate tokens and optional claim-based RBAC |
| Policy section | spec.backend.mcp.authentication | spec.traffic.jwtAuthentication |
| Target ref | AgentgatewayBackend | Gateway or HTTPRoute |
| Client registration | Dynamic registration with IdP | None (client has token) |
For more information, see the JWT auth docs.
Before you begin
- Set up an agentgateway proxy.
- Follow the steps to set up an MCP server with a fetch tool.
- Follow the steps to set up Keycloak.
- Install the experimental channel Gateway API.
kubectl apply --server-side -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/releases/download/v1.4.0/experimental-install.yaml
Configure MCP auth
With Keycloak deployed and your MCP backend configured, you can now create an AgentgatewayPolicy that enforces authentication for the MCP backend.
Create an AgentgatewayPolicy with MCP authentication configuration.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: agentgateway.dev/v1alpha1 kind: AgentgatewayPolicy metadata: name: mcp-echo-authn spec: # Target the MCP backend to apply this authentication policy targetRefs: - group: agentgateway.dev kind: AgentgatewayBackend name: mcp-backend # Configure MCP authentication backend: mcp: authentication: # Issuer URL - must match the 'iss' claim in JWT tokens issuer: "${KEYCLOAK_ISSUER}" # JWKS configuration for token validation jwks: # Reference to the Keycloak service for fetching public keys backendRef: name: keycloak kind: Service namespace: keycloak port: 8080 # Path to the JWKS endpoint on the issuer jwksPath: "${KEYCLOAK_JWKS_PATH}" # Expected audience in JWT tokens audiences: - http://localhost:8080/mcp # Validation mode: Strict requires all claims to be valid mode: Strict # Identity provider type provider: Keycloak # MCP resource metadata for OAuth discovery resourceMetadata: resourceMetadata: # Resource identifier for this MCP server resource: http://localhost:8080/mcp # Scopes supported by this MCP server scopesSupported: - email # Methods for providing bearer tokens bearerMethodsSupported: - header - body - query EOFSetting Description issuerThe OAuth 2.0 issuer URL from your identity provider. This must exactly match the issclaim in JWT tokens. Agentgateway validates this claim to ensure tokens come from the expected identity provider.jwks.backendRefThe Keycloak service. jwks.jwksPathThe path to the JWKS endpoint to obtain public keys. audiencesThe purpose of the JWT token. This value must match the audclaim in JWT tokens.modeThe JWT validation mode. In this example, strict validation is enforced. This mode requires all claims to be valid for agentgateway to proceed with the OAth flow. providerThe identity provider that you use. In this example, Keycloak is used. resourceMetadata.resourceThe identifier for the resource. In this example, the MCP server address is used. resourceMetadata.scopesSupportedThe scopes that the client can request for accessing the MCP server. resourceMetadat.bearerMethodsSupportedMethods to provide the bearer token when authenticating with the server. In this example, the bearer token can be provided as a header, query parameter, or as part of the body. Verify that the policy was accepted.
kubectl get AgentgatewayPolicy mcp-echo-authn -o yamlUpdate the HTTPRoute that routes incoming traffic to the MCP server to include the discovery paths for the MCP resource and authorization server. This way, the agentgateway proxy can retrieve the resource and authorization server metadata during the MCP auth flow.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: HTTPRoute metadata: name: mcp spec: # Reference the Agentgateway parentRefs: - group: gateway.networking.k8s.io kind: Gateway name: agentgateway-proxy namespace: agentgateway-system rules: - filters: # Enable CORS for browser-based MCP clients - type: CORS cors: allowCredentials: true allowHeaders: - Origin - Authorization - Content-Type allowMethods: - "*" allowOrigins: - "*" exposeHeaders: - Origin - X-HTTPRoute-Header maxAge: 86400 # Route to the MCP backend backendRefs: - group: agentgateway.dev kind: AgentgatewayBackend name: mcp-backend # Match MCP and OAuth discovery paths matches: # Main MCP endpoint to connect to the MCP server - path: type: PathPrefix value: /mcp # Path to access resource server metadata - path: type: PathPrefix value: /.well-known/oauth-protected-resource/mcp # Path to access authorization server metadata - path: type: PathPrefix value: /.well-known/oauth-authorization-server/mcp # JWKS endpoint for token validation - path: type: PathPrefix value: /realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/certs EOF
Verify MCP auth
Open the MCP inspector.
npx modelcontextprotocol/inspector#0.18.0From the MCP Inspector menu, connect to your agentgateway address as follows:
- Transport Type: Select
Streamable HTTP. - URL: Enter the agentgateway address, port, and the /mcp path. If your agentgateway proxy is exposed with a LoadBalancer server, use
http://${INGRESS_GW_ADDRESS}/mcp. In local test setups where you port-forwarded the agentgateway proxy on your local machine, usehttp://localhost:8080/mcp. - Click Connect.
Verify that the connection fails, because authentication is required to access the MCP server.
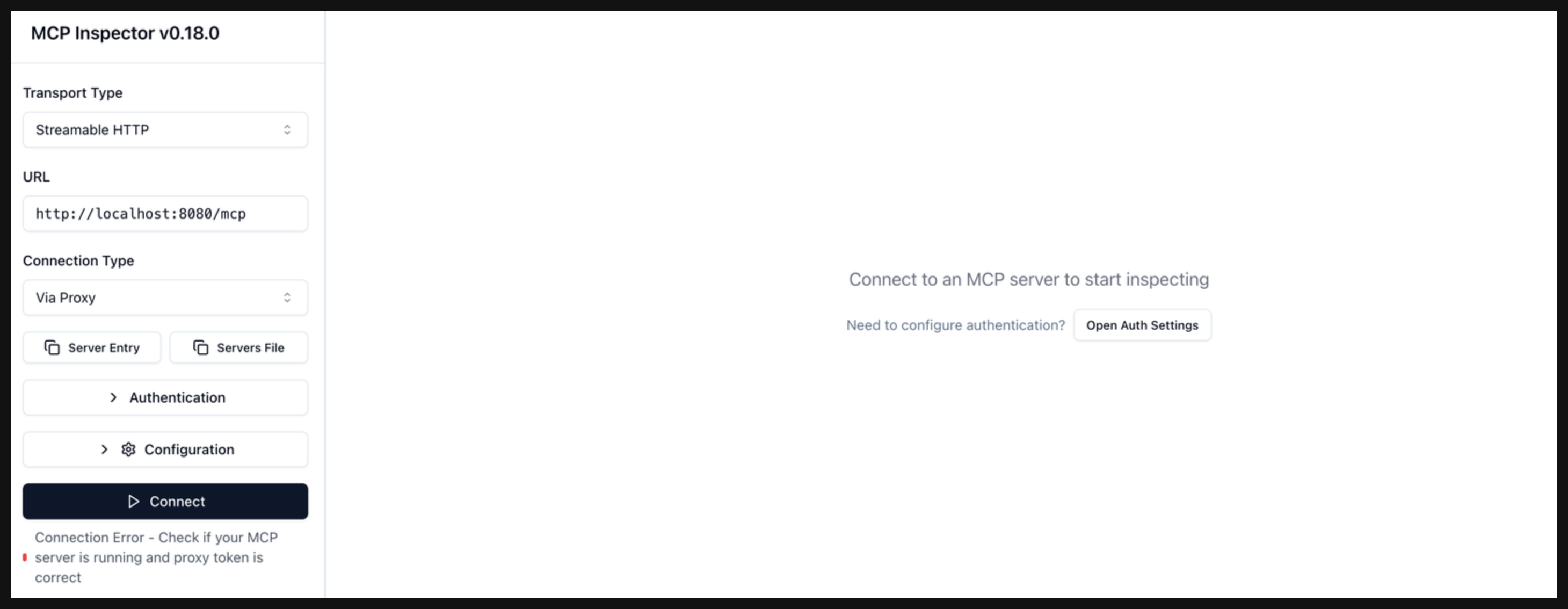
- Transport Type: Select
Click Open Auth Settings to run through the MCP Auth flow that you configured with the agentgateway proxy.
Run through the auth flow. You can decide to manually run through the auth flow or select Quick OAuth Flow to automatically run through all the auth steps automatically. This guide assumes that you run through the auth flow manually.
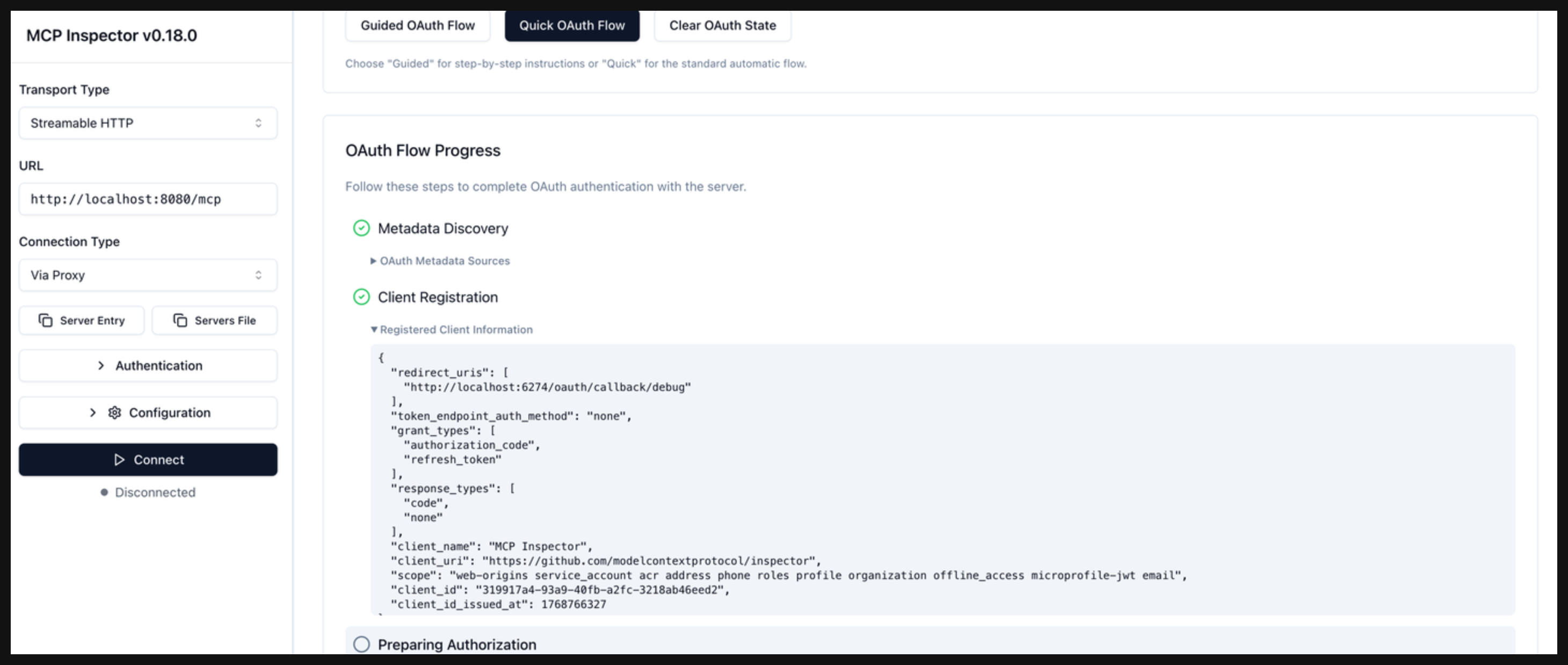
In the OAuth Flow Progress card, click Continue to start the Metadata Discovery phase. Verify that the step succeeds and that you see the authorization server metadata. The metadata include information about the location of the authorization server, supported scopes, and ways to provide the bearer token.
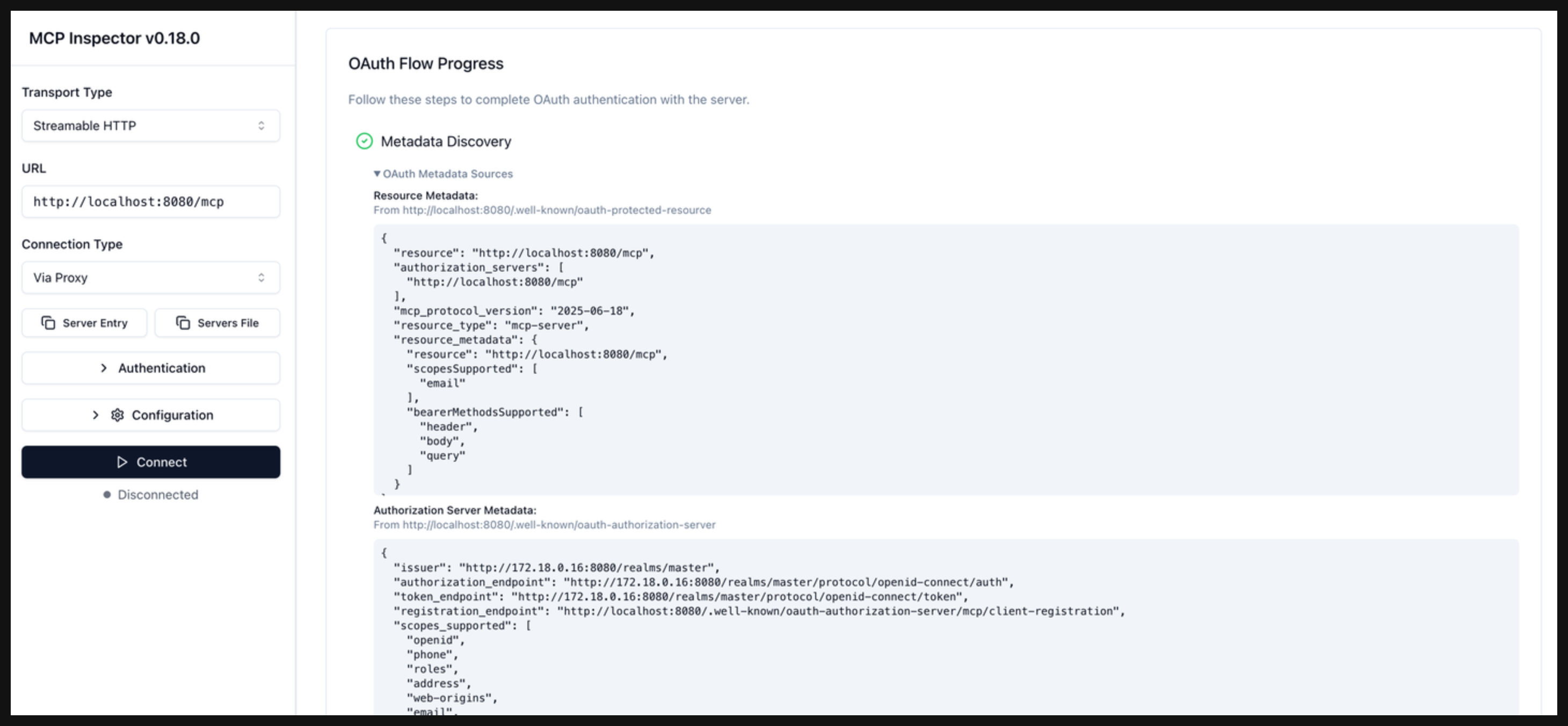
Click Continue to start the Client registration phase. Verify that the MCP inspector tool successfully registered as a client in Keycloak and is assigned a client ID.
Click Continue to start the Preparing Authorization phase. Verify that you get back a URL to log in to Keycloak with your credentials. Open the link in your browser and log in with the user
user1and passwordpassword.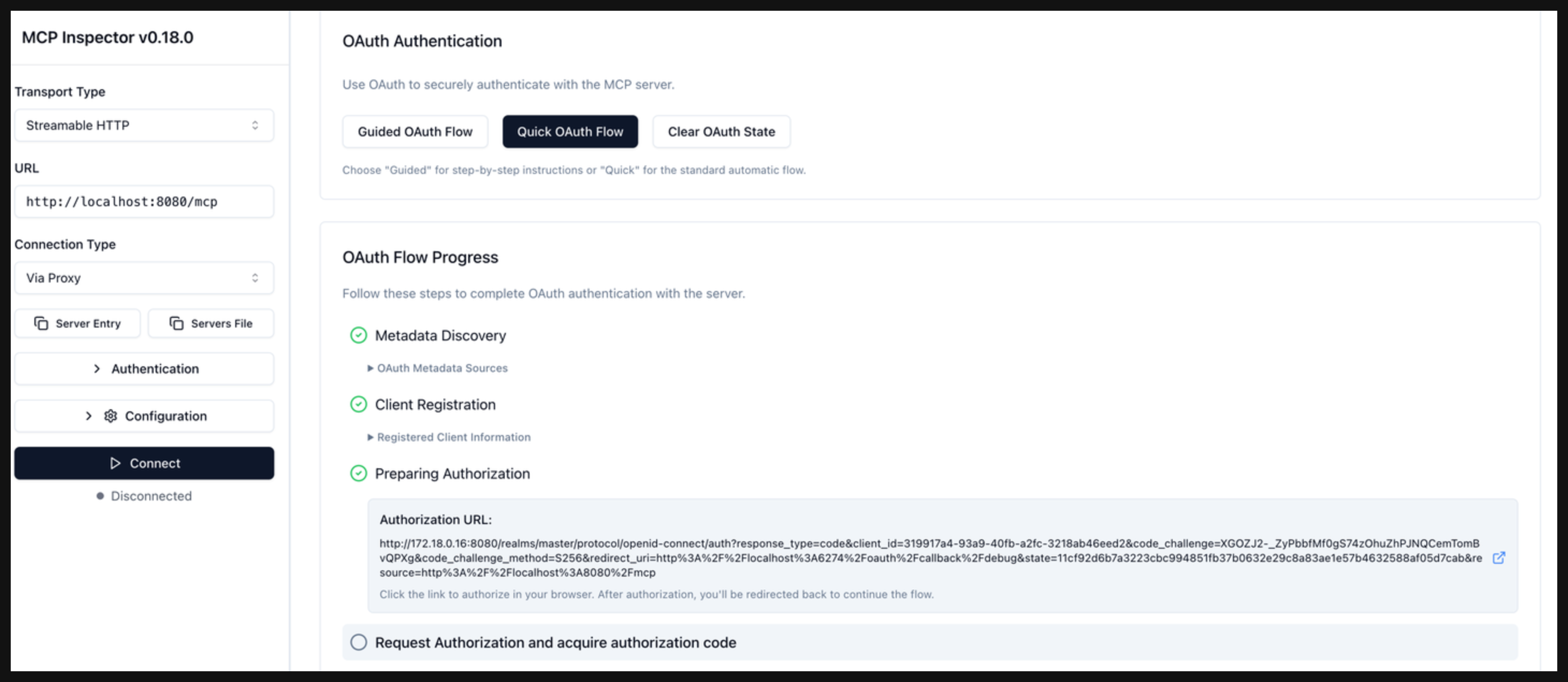
After you log in to Keycloak, an authorization code is displayed. Copy the authorization code and continue with the next step.
Copy the authorization code into the Authorization Code field in the MCP inspector. Then, click Continue to start the Request Authorization and acquire authorization code phase.
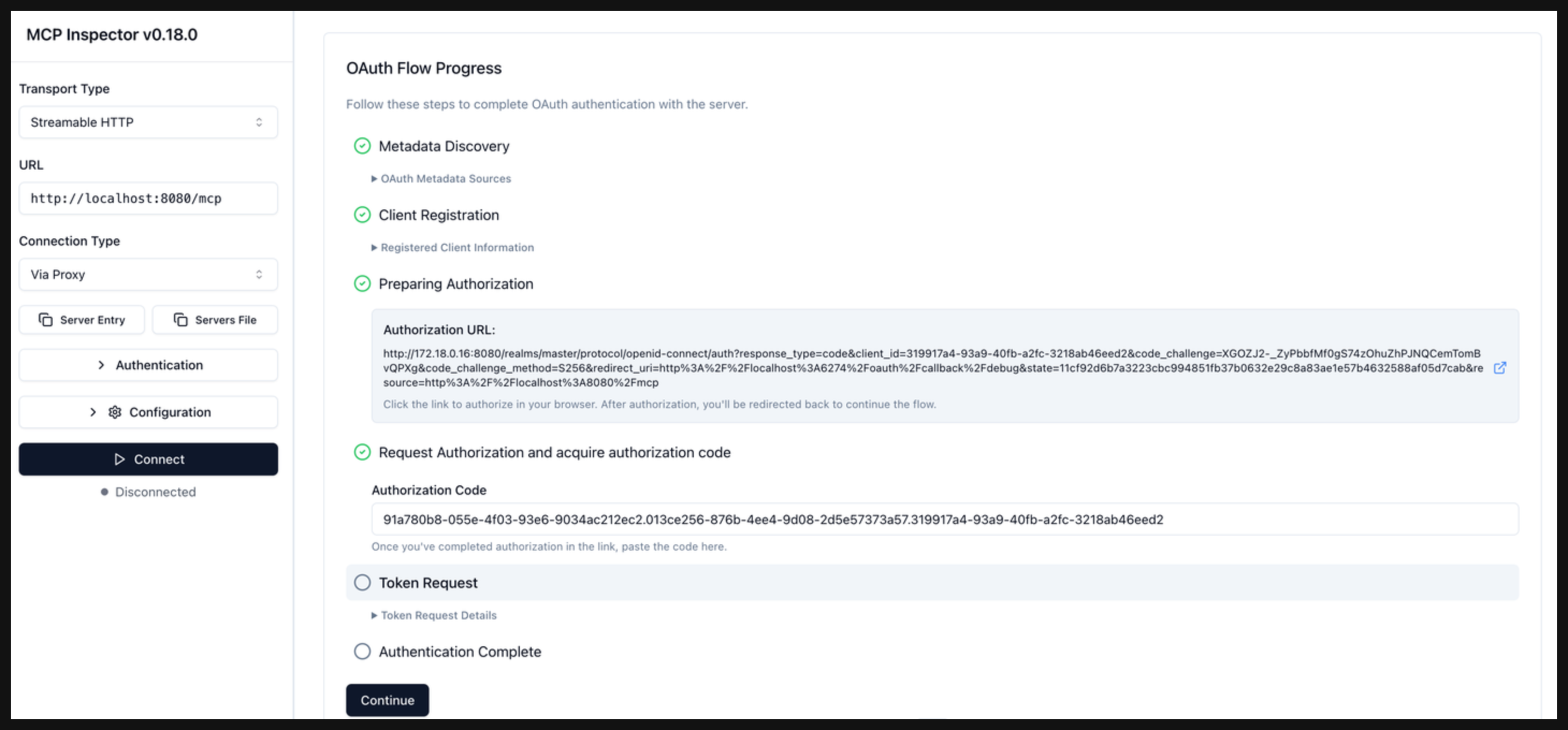
Click Continue to start the Token Request phase. In this phase, the authorization code is exchanged for a token. Verify that the Authentication Complete phase succeeds and that you get back a token from Keycloak.
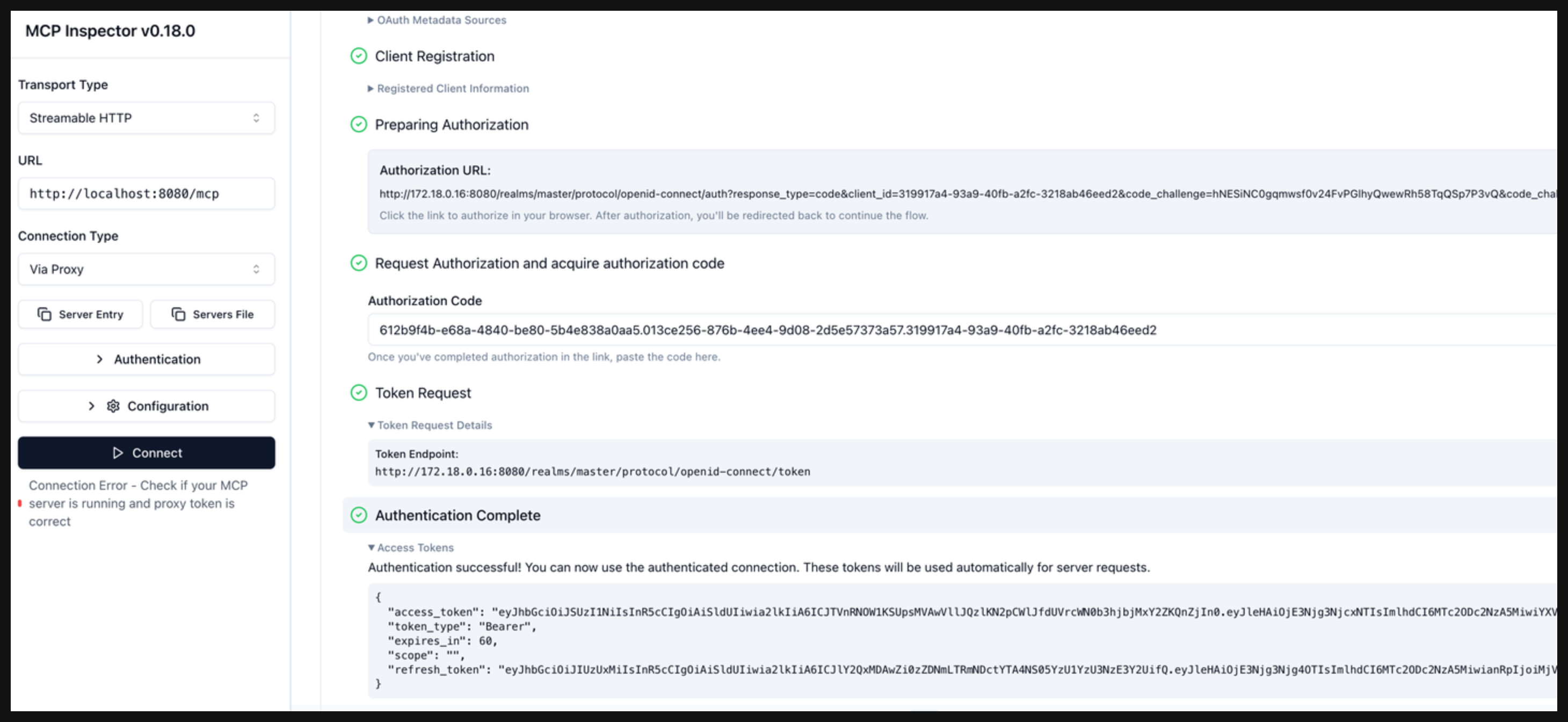
Connect to your MCP server.
- Copy the
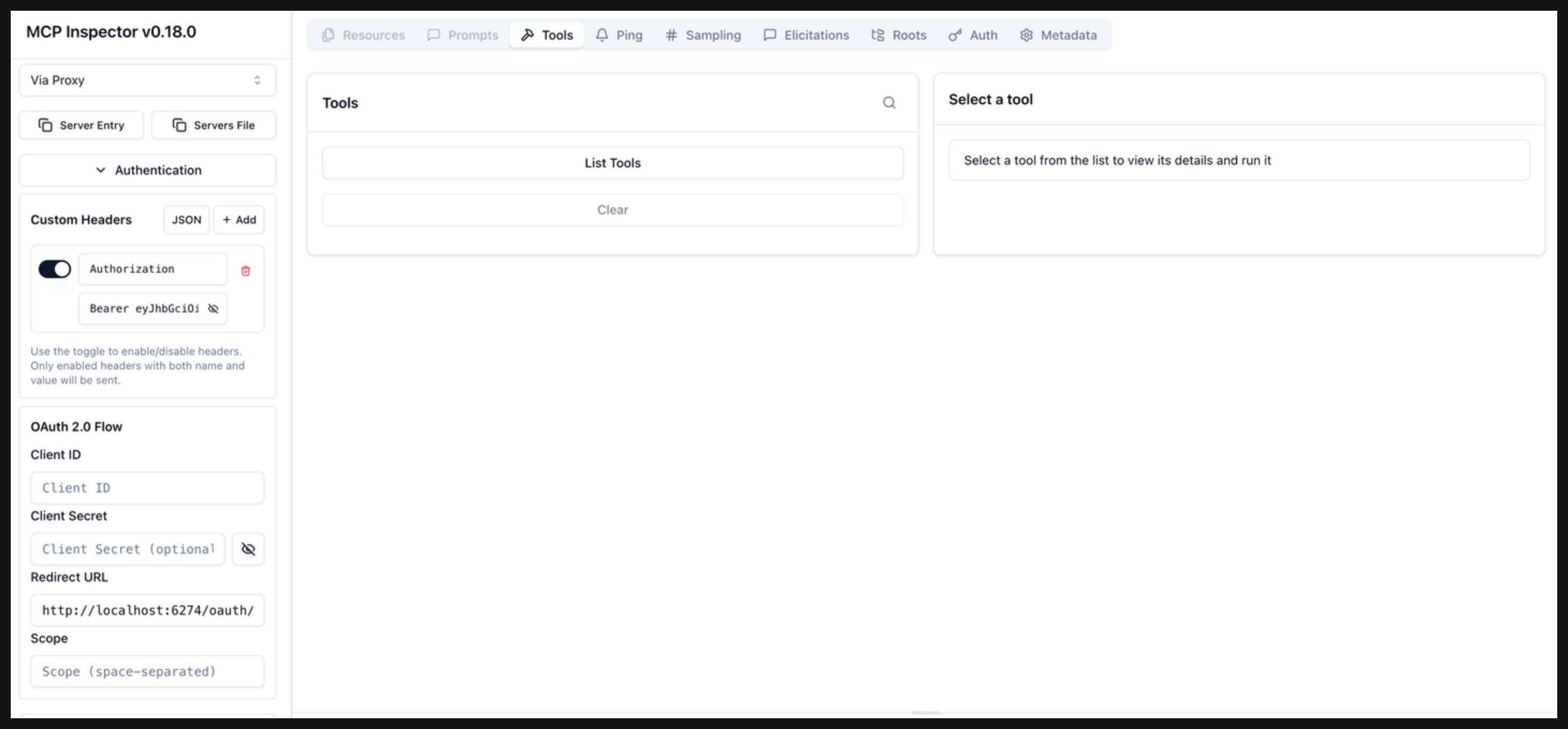
access_tokenvalue from the Authentication Complete phase. - Open the Authentication section in the MCP inspector.
- In the Custom Headers card, click Add.
- Add the following values:
- header name:
Authorization - header value:
Bearer <value of access_token>
- header name:
- Click Connect to connect to your MCP server.
- Copy the
Clean up
You can remove the resources that you created in this guide.kubectl delete AgentgatewayPolicy mcp-echo-authn
kubectl delete httproute mcp