Routes
Routes Route A rule that matches incoming requests and forwards them to backends. Routes can match on path, hostname, headers, query parameters, and HTTP methods. are the entry points for traffic to your agentgateway. They are configured on listeners and are used to route traffic to backends Backend A destination service that receives traffic from agentgateway. Backends can be static hosts, MCP servers, LLM providers, or other services. .
You can use the built-in agentgateway UI or a configuration file to create, update, and delete routes.
Types of routes
You can configure two types of routes: HTTP routes (routes) and TCP routes (tcpRoutes).
HTTP routes
HTTP or HTTPS listeners use routes to configure HTTP routes. HTTP routes support all HTTP features such as path, header, method, or query
matching
Matching
The process of determining which route should handle an incoming request based on criteria such as path, hostname, headers, query parameters, or HTTP methods.
, and HTTP-specific filters and
policies
Policy
A configuration that manipulates, secures, or observes traffic as it flows through agentgateway. Policies can be attached at the listener, route, or backend level.
.
Example configuration:
# yaml-language-server: $schema=https://agentgateway.dev/schema/config
binds:
- port: 8080
listeners:
- name: http-proxy
protocol: HTTP
routes:
- name: http-backend
backends:
- host: http.example.com:8080
weight: 1For more information, continue to the Create routes section.
TCP routes
TCP listeners use tcpRoutes instead of routes. TCP routes have a simpler structure than other HTTP routes.
Keep in mind that TCP routes do not support HTTP features such as path, header, method, or query matching, and HTTP-specific filters and policies.
Example configuration:
# yaml-language-server: $schema=https://agentgateway.dev/schema/config
binds:
- port: 5432
listeners:
- name: postgres-proxy
protocol: TCP
tcpRoutes:
- name: postgres-backend
backends:
- host: postgres.example.com:5432
weight: 1For more information, see TCP route matching.
Before you begin
Create routes
Set up a route on your listener.
Download a configuration file for your agentgateway.
curl -L https://agentgateway.dev/examples/basic/config.yaml -o config.yamlReview the configuration file.
cat config.yamlbinds: - port: 3000 listeners: - routes: - policies: cors: allowOrigins: - "*" allowHeaders: - mcp-protocol-version - content-type - cache-control exposeHeaders: - "Mcp-Session-Id" backends: - mcp: targets: - name: everything stdio: cmd: npx args: ["@modelcontextprotocol/server-everything"]Run the agentgateway.
agentgateway -f config.yamlOpen the agentgateway route UI.
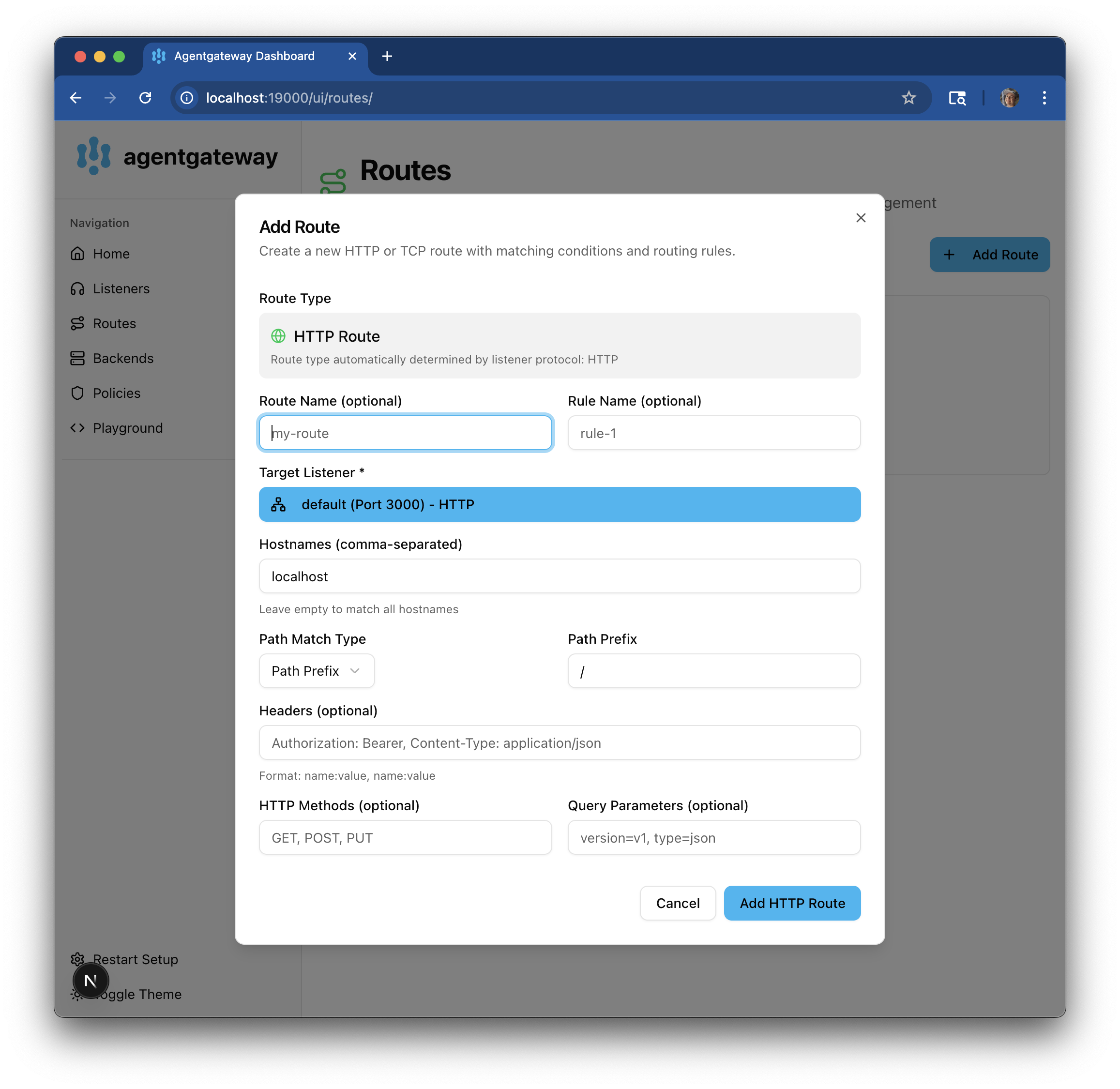
Click Add Route and configure a route such as follows:
- Name: An optional name for the route.
- Rule Name: An optional name for the matching rules of the route.
- Target Listener: Select the listener that you previously created. The Route Type is automatically determined based on the listener protocol.
- Hostnames: Add the hostnames that the route serves traffic on.
- Path Match Type: Select the type of path matching that you want to use, such as
Path Prefix, and then configure its details. For more options, see the Request matching guide. - Headers: Optional header configuration, such as the authorization header.
- HTTP Methods: Optional HTTP methods to allow, such as
GET, POST, PUT. - Query Parameters: Optional query parameters to allow, such as
version=v1. - Click Add HTTP Route to continue.
Download a configuration file that contains your route configuration.
curl -L https://agentgateway.dev/examples/basic/config.yaml -o config.yamlReview the configuration file. The example sets up an HTTP listener on port 3000 that matches on all hosts. For more options, see the Request matching guide.
cat config.yamlbinds: - port: 3000 listeners: - routes: - policies: cors: allowOrigins: - "*" allowHeaders: - mcp-protocol-version - content-type - cache-control exposeHeaders: - "Mcp-Session-Id" backends: - mcp: targets: - name: everything stdio: cmd: npx args: ["@modelcontextprotocol/server-everything"]Run the agentgateway.
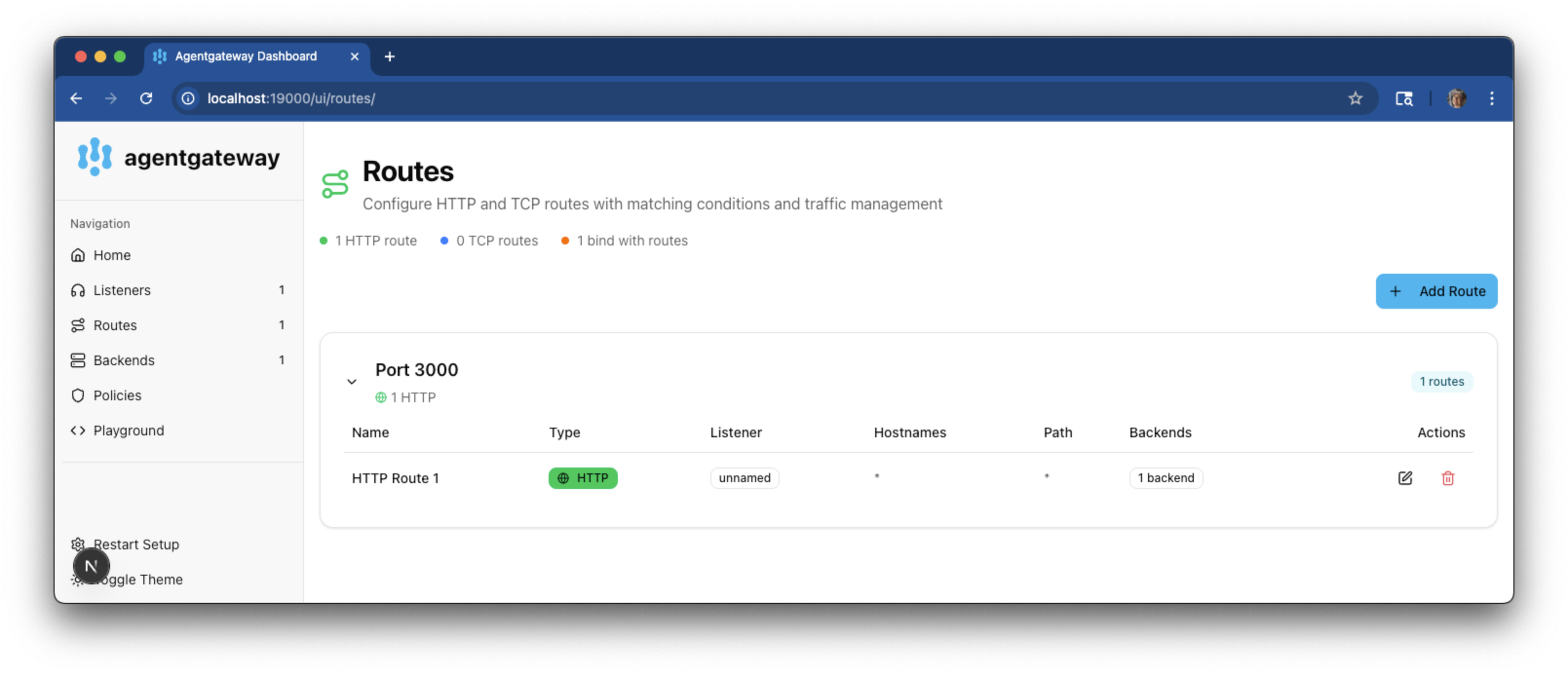
agentgateway -f config.yamlOpen the agentgateway listener UI and verify that your route is added successfully.
Delete routes
Remove agentgateway routes by using the UI or deleting the configuration file.
Remove agentgateway routes with the UI.
Run the agentgateway from which you want to remove a route.
agentgateway -f config.yamlOpen the agentgateway route UI and find the route that you want to remove.

Click the trash icon to remove the route.
Update the configuration file to remove the route.
Remove the route from your configuration file.
Apply the updated configuration file to your agentgateway.
agentgateway -f config.yaml
Next steps
After you create routes, you might want to apply policies to them.