TCP listeners
You can use the built-in agentgateway UI or a configuration file to create, update, and delete TCP listeners. TCP listeners enable raw TCP connection proxying for non-HTTP protocols.
About
TCP listeners provide raw TCP connection proxying, which is useful for:
- Database connections: Proxy PostgreSQL, MySQL, Redis, and other database protocols
- Custom protocols: Handle any TCP-based protocol that isn’t HTTP
- Legacy applications: Connect older applications that use custom TCP protocols
- TLS termination: Terminate TLS connections and forward to backend services
- TLS passthrough: Route TLS connections based on their SNI, without terminating the TLS connection, and forward to backend services
Before you begin
Install theagentgateway binary.
Create listeners
Set up a TCP listener on your agentgateway.
-
Create a configuration file with your TCP listener configuration.
cat > config.yaml << 'EOF' # yaml-language-server: $schema=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/agentgateway/agentgateway/refs/heads/main/schema/local.json binds: - port: 5432 listeners: - name: postgres-proxy protocol: TCP tcpRoutes: - name: postgres-backend backends: - host: postgres.example.com:5432 weight: 1 EOF -
Review the configuration file. The example sets up a TCP listener that proxies raw TCP connections on port 5432 to a PostgreSQL server.
cat config.yaml# yaml-language-server: $schema=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/agentgateway/agentgateway/refs/heads/main/schema/local.json binds: - port: 5432 listeners: - name: postgres-proxy protocol: TCP tcpRoutes: - name: postgres-backend backends: - host: postgres.example.com:5432 weight: 1 -
Run the agentgateway.
agentgateway -f config.yaml -
Open the agentgateway listener UI.
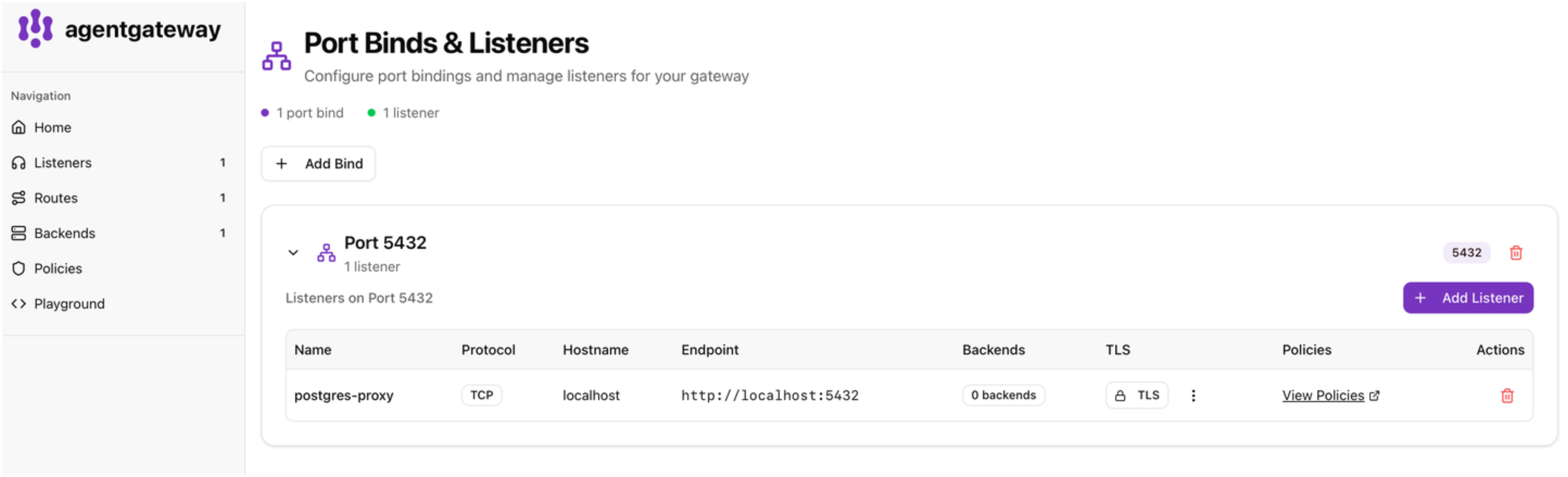
-
Click Add Bind.
-
Enter a Port number such as
5432and then click Add Bind.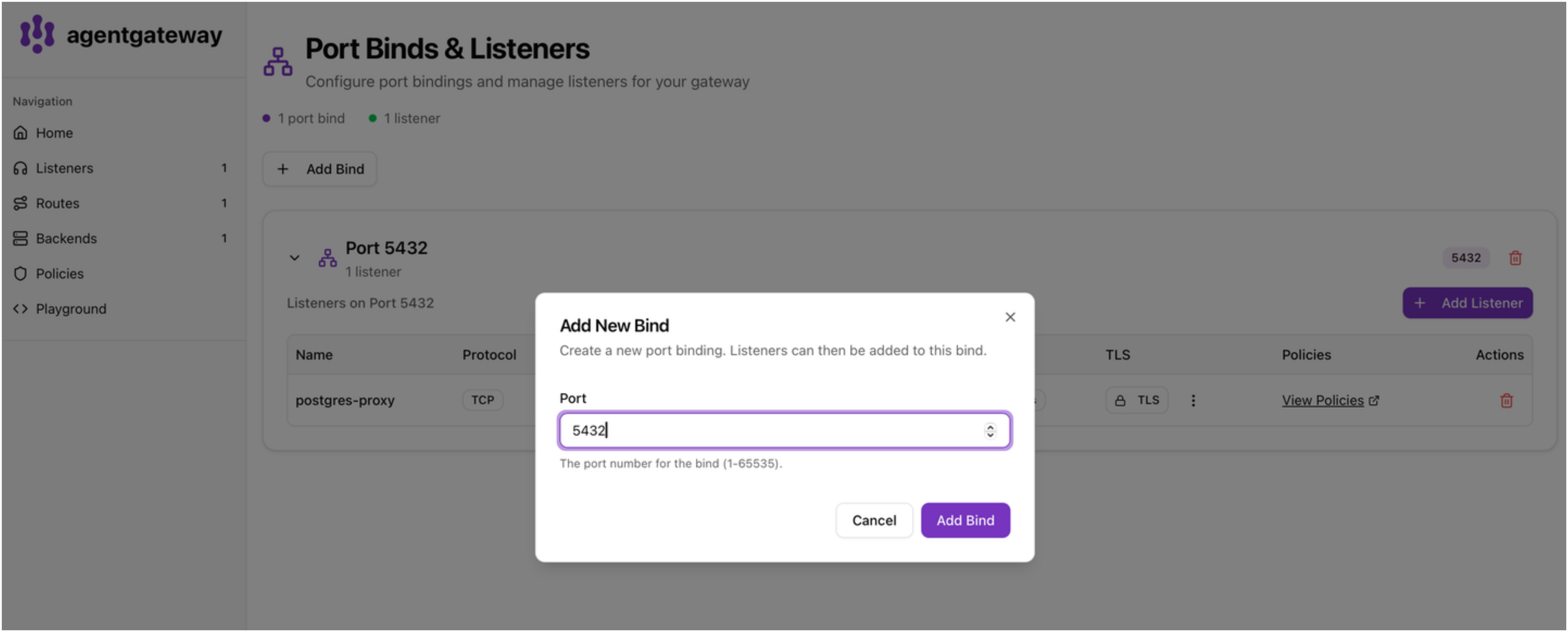
-
Expand the port that you just created and click Add Listener.
-
For your listener, configure the details.
- Name: If you omit this, a name is generated for you.
- Gateway Name: An optional field to group together listeners for ease of management, such as listeners for the same app or team.
- Target Bind: The port bind that you set up in the previous step.
- Protocol: Select
TCPas the protocol. - Hostname: The hostname that the listener binds to, which can include a wildcard
*. To use an address that is compatible with IPv4 and IPv6, enter[::]. - Click Add Listener to save your configuration.
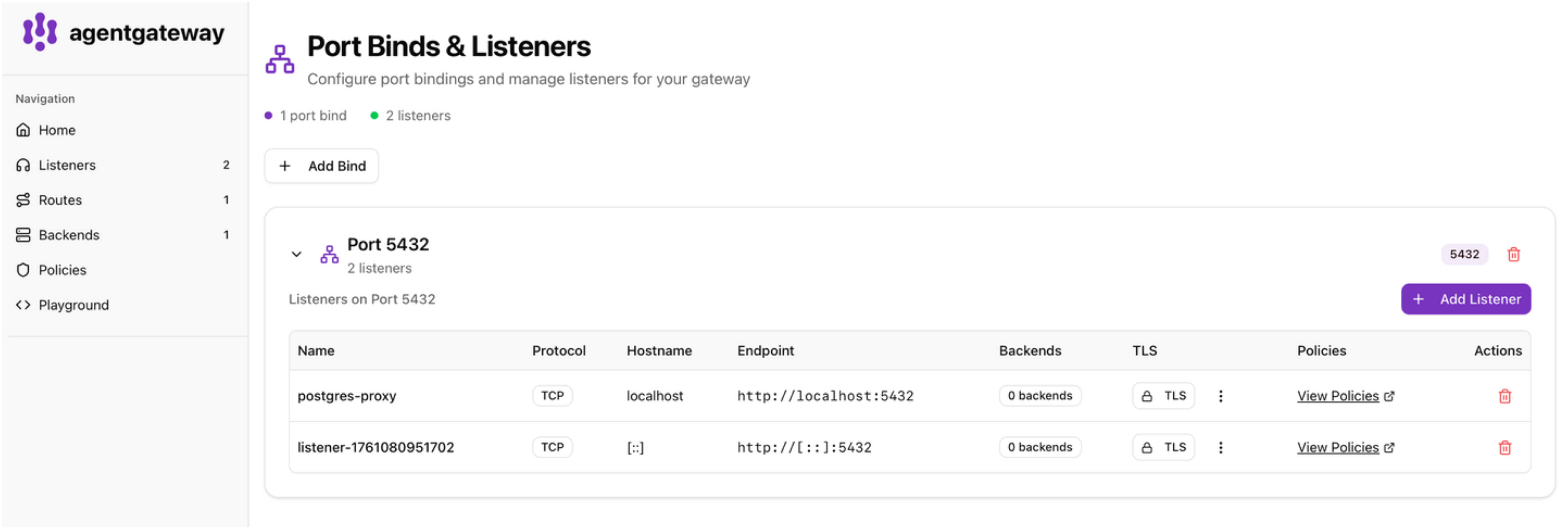
-
Create a configuration file with your TCP listener configuration.
cat > config.yaml << 'EOF' # yaml-language-server: $schema=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/agentgateway/agentgateway/refs/heads/main/schema/local.json binds: - port: 5432 listeners: - name: postgres-proxy protocol: TCP tcpRoutes: - name: postgres-backend backends: - host: postgres.example.com:5432 weight: 1 EOF -
Review the configuration file. The example sets up a TCP listener that proxies raw TCP connections on port 5432 to a PostgreSQL server.
cat config.yaml# yaml-language-server: $schema=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/agentgateway/agentgateway/refs/heads/main/schema/local.json binds: - port: 5432 listeners: - name: postgres-proxy protocol: TCP tcpRoutes: - name: postgres-backend backends: - host: postgres.example.com:5432 weight: 1 -
Run the agentgateway.
agentgateway -f config.yaml -
Open the agentgateway listener UI and verify that your TCP listener is added successfully.
Delete listeners
Remove agentgateway TCP listeners by using the UI or deleting the configuration file.
Remove agentgateway TCP listeners with the UI.
-
Run the agentgateway from which you want to remove a listener.
agentgateway -f config.yaml -
Open the agentgateway listener UI and find the TCP listener that you want to remove.
-
Click the trash icon and then Delete to remove the listener.
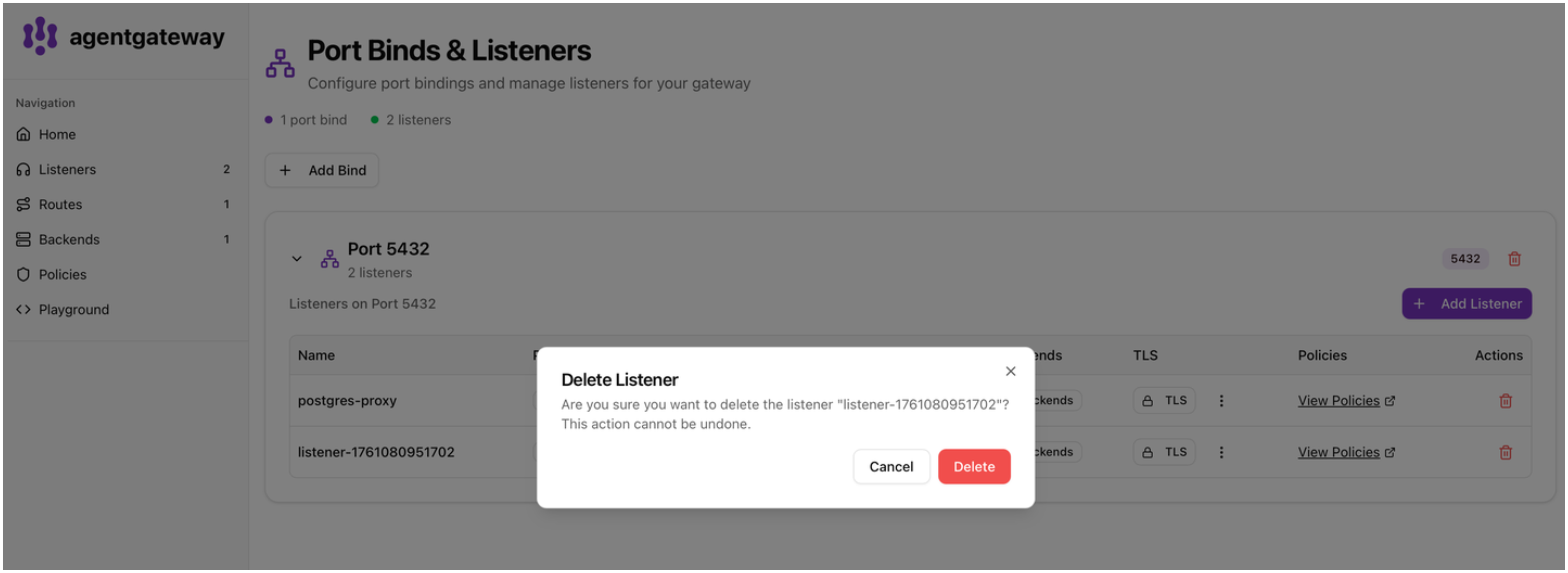
Update the configuration file to remove the TCP listener.
-
Remove the TCP listener from your configuration file.
-
Apply the updated configuration file to your agentgateway.
agentgateway -f config.yaml
Next steps
Create a TCP route on the listener.